Understanding the Basics of Artificial Intelligence
Have you ever wondered about the magic behind those chatbots (like chat GPT)?
…and how they seem to know exactly what you’re looking for.
Or how Netflix or Youtube suggests the perfect series or video just for you?
All that is down to Artificial Intelligence, lovingly known as AI.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, AI has become more than just a buzzword,
…it’s a revolutionary force that’s transforming industries worldwide.
From healthcare to finance, entertainment to manufacturing,
AI is changing the way we live, work, and play.
Imagine a world where machines can think, learn, and make decisions like humans – that’s the heart of AI.
For some people, this concept can feel a bit freaky.
While in reality, like most tools, it can be used for good or bad.
But fear not, we’re not diving into the deep end just yet.
The goal here is to break down complex concepts into bite-sized pieces that make sense of AI.
Whether you’re an AI novice or just looking to brush up on the basics, this article is designed to help you understand AI from the ground up.
By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to hold your own in AI conversations and navigate this exciting field with confidence.
Ready? Let’s start unravelling the world of AI.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Imagine if your computer could understand your emotions, learn from experience, and make decisions just like you do. That’s the essence of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI is all about teaching machines to think and act intelligently, in a way that imitates human intelligence.
Defining AI: AI is the art of creating smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks range from recognising patterns in data, solving complex problems, making predictions, understanding natural language, and even adapting and learning from new information.
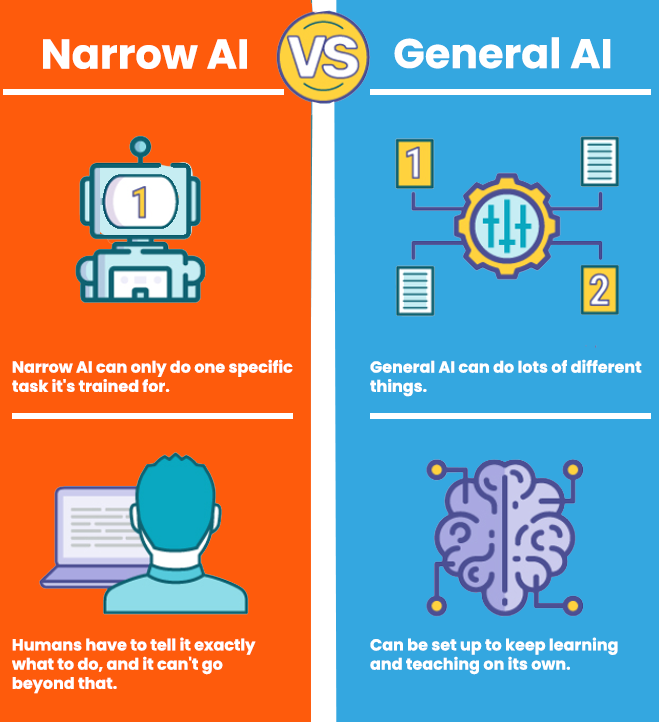
Narrow vs. General AI: Now, picture AI as a spectrum. On one end, we have narrow AI, also known as weak AI. This type of AI is designed for specific tasks and excels in them. Think of virtual assistants like Siri or chatbots that help with customer queries. They’re great at what they do, but they lack the broader understanding and consciousness of human intelligence.
On the other end, there’s general AI, also called strong or super AI. This is the AI you often see in science fiction – machines that possess human-like cognitive abilities, can understand a wide range of tasks, and have a level of consciousness. We’re not quite there yet, and this is where most of the futuristic AI scenarios come into play.
4 Common Misconceptions about AI
I know a lot of people who are very sceptical about AI, and quite rightly so. There are so many crazy movies out there about robots and AI, plus it’s completely new to most people. That’s why it’s important to learn the facts about AI, rather than being distracted with the fiction shown in Hollywood.
- AI Equals Human Intelligence – One of the most common misconceptions is that AI is on par with human intelligence. While AI can perform certain tasks exceptionally well, it’s not synonymous with human-level understanding, emotions, or creativity. However, in saying this chat GPT 4 has passed many degrees at this point (more about that later).
- AI Will Take Over the World – You’ve probably heard stories of AI-powered robots becoming rulers of the world in movies. But in reality, AI is a tool created and controlled by humans. Its impact, whether positive or negative, largely depends on how it’s developed and utilised. That’s why there’s a lot of debate going on right now about mitigating AI bias and ethics.
- AI Always Gets It Right – AI isn’t infallible. It learns from data, and if that data is biassed or incomplete, AI can make flawed decisions. I suppose this is like humans when they don’t quite know about the topic they’re discussing. It’s important to remember that AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on.
- AI Will Replace All Jobs – While AI can automate repetitive and mundane tasks with ease, it’s also creating new job roles. The aim is to complement human capabilities, not replace them. AI can handle tasks that are time-consuming or data-driven, freeing up humans to focus on higher-level tasks that require creativity and emotional intelligence. This should allow a lot of humans to escape the dread of work, and instead step into a dream career, should they wish.
As we embark on this AI journey, keep in mind that AI’s true potential lies in its ability to enhance our lives, solve complex problems, and make processes more efficient.
Would you like help deploying AI, and automation in your business? Contact us today for a free consultation
The 4 Pillars of AI: Machine Learning and Deep Learning
The idea with AI is that computers can evolve and become smarter with experience. Just like humans do. This happens with the power of Machine Learning (ML), a pivotal subset of AI. And within the world of ML, there’s a dynamic field that’s taking AI to new heights: Deep Learning.
1. Machine Learning: Learning from Data
Machine Learning is like a digital brain that learns from patterns. Imagine you’re teaching a child to identify animals. You show them pictures of cats and dogs, and over time, they learn to distinguish between the two. Similarly, ML algorithms work by being fed tons of data and learning from it.
2. Algorithmic Magic: Training Models
These algorithms are like the wizards behind the curtain, transforming raw data into predictions and decisions. Think of them as recipes that the computer follows to process data. Much like chat GPT prompts. The more accurate the recipe (or prompt), the better the outcome. For instance, an algorithm can learn to predict whether an email is spam or not based on certain keywords.
>>Download 100 Chat GPT Prompts for Business<<
3. Deep Learning: Unleashing Neural Networks
Now, let’s talk about Deep Learning, the rockstar of ML. Imagine your brain, it’s made up of interconnected neurons that process information. Deep Learning mimics this neural structure in its artificial networks called neural networks. But instead of a few connections, these networks have layers upon layers, creating a complex web of information processing.
4. Layers of Abstraction: Getting Deeper
Each layer of a neural network extracts specific features from the data that’s been imputed. If we’re identifying objects in images, the first layer might focus on edges, the second on shapes, and so on. As you move deeper into the network, the abstractions become more intricate. This ability to grasp high-level concepts in data is why deep learning has brought us breakthroughs in areas like image recognition and natural language understanding.
In a nutshell, while Machine Learning gives computers the power to learn from data and make predictions, Deep Learning kicks it up a notch by creating intricate, multi-layered models that can unravel complex patterns. These pillars form the backbone of AI’s impressive capabilities.
Key AI Techniques and Approaches
Picture AI as a toolkit filled with a variety of techniques, each designed to tackle different challenges. Let’s unpack some of these techniques that form the building blocks of AI’s capabilities.
Supervised Learning: Guided Learning from Data
Imagine a teacher guiding a student step-by-step. Supervised learning is similar—it’s like training a model with a coach by its side. Here’s how it works: the model is given labelled examples, which means it’s shown inputs along with the correct outputs. Over time, the model learns to associate the inputs with the correct answers. It’s like teaching a child to identify different colours by showing them pictures with labels: “This is red, and that’s blue,” for example.
Unsupervised Learning: Unearthing Hidden Patterns
Let’s venture into unsupervised learning, and the realm of data exploration. Imagine you’re handed a bunch of jigsaw puzzle pieces without a picture to guide you. Your task? Group the pieces that fit together. Unsupervised learning does something similar with data—it identifies patterns and structures without the help of labelled outputs. It’s like AI saying, “Let’s find out how these pieces relate to each other.”
Reinforcement Learning: Learning by Doing
Remember learning to ride a bike? You probably fell a few times before mastering the art of cycling. Reinforcement learning mimics this trial-and-error process. It’s like an AI agent exploring an environment. It takes actions and receives rewards or penalties based on its choices. Over time, it learns to make better decisions to maximise rewards and minimise penalties. It’s like teaching a robot to navigate a maze, where it gets a treat when it chooses the right path.
The 4 Major Components of AI Applications
In short there are four components of all AI applications – Input, Algorithm, Model and Output, as described below:-
Input Data: Every AI application starts with data. It’s the raw material that AI algorithms chew on to learn and make decisions.
Algorithm: Think of algorithms as the magic spells that transform data into insights. Each algorithm has a unique recipe for processing and analysing data
Model: The model is the AI’s interpretation of reality. It’s like an artist’s canvas where the algorithm paints the patterns and relationships it discovers in the data
Output: The grand finale! The output is what you get after the AI algorithm has worked its magic. It could be a prediction, a decision, or a recommendation.
In Conclusion
There are many layers to AI, and it’s taking the world by storm. Hence it pays to understand the basics. Both AI and automation can greatly enhance business outcomes in a wide range of ways. For example it can make large mundane tasks a breeze and minimise error. This article has outlined the basics, so that you know a bit more about how it all works.
